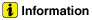Hyundai Palisade: Exhaust Emission Control System / CVVT (Continuous Variable Valve Timing) System
Hyundai Palisade (LX2) 2020-2025 Service Manual / Emission Control System / Exhaust Emission Control System / CVVT (Continuous Variable Valve Timing) System
Description and operation
| Description |
Continuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT) system advances or retards the valve
timing of the intake and exhaust valve in accordance with the ECM control signal
which is calculated by the engine speed and load.
By controlling CVVT, the valve over-lap or under-lap occurs, which makes better
fuel economy and reduces exhaust gases (NOx, HC) and improves engine performance
through reduction of pumping loss, internal EGR effect, improvement of combustion
stability, improvement of volumetric efficiency, and increase of expansion work.
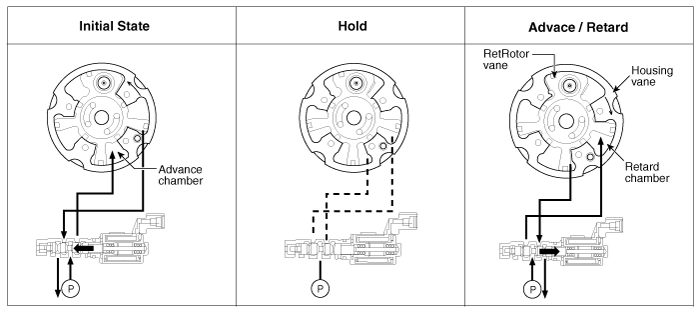
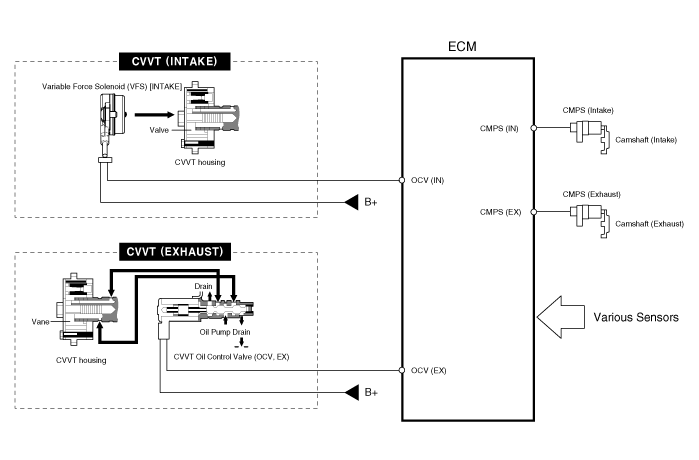
This system consists of the CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) which supplies the
engine oil to the cam phaser or takes out the engine oil from the cam phaser
in accordance with the ECM PWM (Pulse With Modulation) control signal, the CVVT
Oil Temperature Sensor (OTS) which measures the engine oil temperature, and
the Cam Phaser which changes the cam phase by using the hydraulic force of the
engine oil.
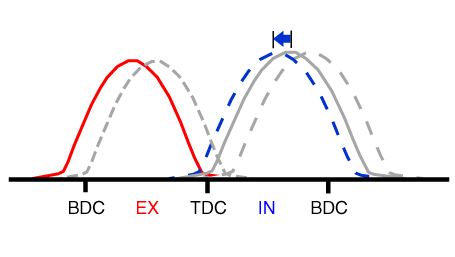
The engine oil which is supplied from the CVVT oil control valve changes the
cam phase in the direction (Intake Advance/Exhaust Retard) or opposite direction
(Intake Retard/Exhaust Advance) of the engine rotation by rotating the rotor
connected with the camshaft inside the cam phaser.
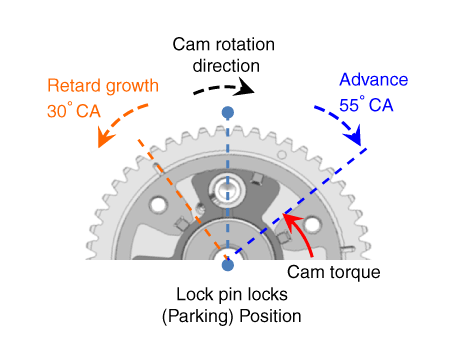
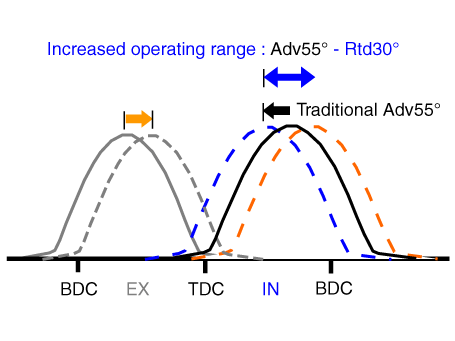
| [Intermediate Lock CVVT] |
It increases the retarded amount compared to the default state to expand the
operating range of the variable valve timing system.
The cam phase is fixed mechanically so that it is locked at the middle position.
|
|
▷Effect Improves fuel efficiency by approx. 1.7%. Expands the intake CVVT operating range. (Increases the retarded amount by up to 30° compared to the default state.) ∇ LIVC (Late Intake Valve Close) ∇ 1. Improves fuel efficiency by reducing pumping loss. 2. Improves knocking characteristics by reducing compression ratio. |
|
|
|
|
Default position : Middle CVVT operates in advanced / retarded directions. |
| Operation Principle |
The CVVT has the mechanism rotating the rotor vane with hydraulic force generated
by the engine oil supplied to the advance or retard chamber in accordance with
the CVVT oil control valve control.
|
| 1. |
Intake CVVT
|
| 2. |
Exhaust CVVT
|
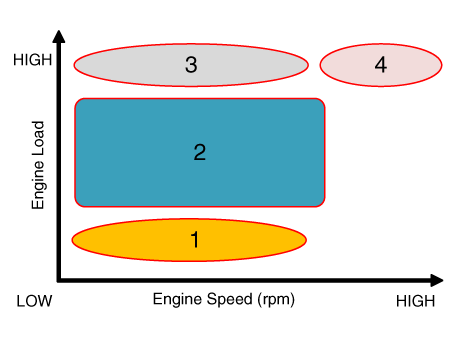
[CVVT System Mode]
|
(1) Low Speed / Low Load |
(2) Part Load |
|
|
|
|
(3) Low Speed / High Load |
(4) High Speed / High Load |
|
|
|
|
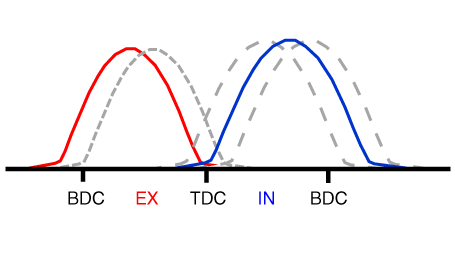
Driving Condition |
Exhaust Valve |
Intake Valve |
||
|
Valve Timing |
Effect |
Valve Timing |
Effect |
|
|
(1) Low Speed /Low Load |
Completely Advance |
* Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability |
Completely Retard |
* Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability |
|
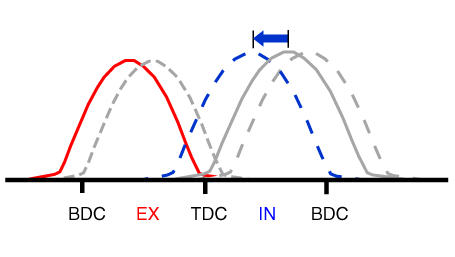
(2) Part Load |
Retard |
* Increase of expansion work * Reduction of pumping loss * Reduction of HC |
Retard |
* Reduction of pumping loss |
|
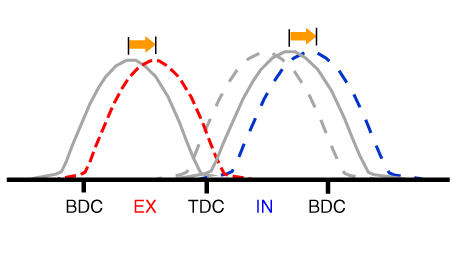
(3) Low Speed /High Load |
Retard |
* Increase of expansion work |
Advance |
* Prevention of intake back flow (Improvement of volumetric efficiency) |
|
(4) High Speed /High Load |
Advance |
* Reduction of pumping loss |
Retard |
* Improvement of volumetric efficiency |
Schematic diagrams
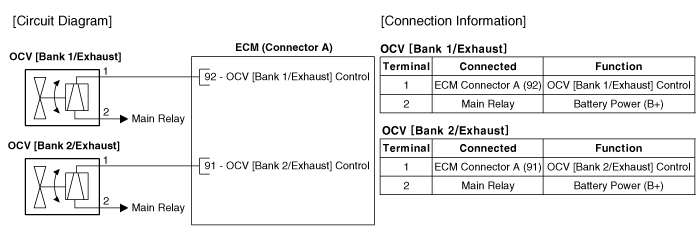
| Circuit Diagram |
| Variable Force Solenoind (VFS) |
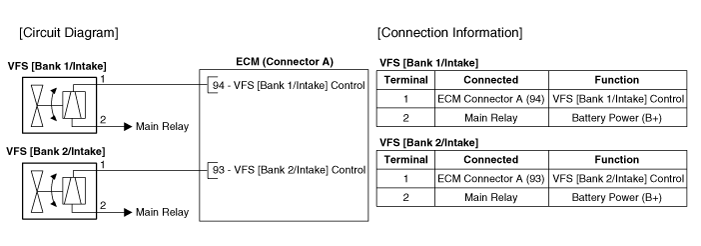
Harness Connector
| CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) |
Harness Connector
Repair procedures
| Inspection |
| Variable Force Solenoind (VFS) |
Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "E-CVVT Motor"
| CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) |
Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV)"
| Removal |
| Variable Force Solenoind (VFS) |
Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "E-CVVT Motor"
| CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) |
Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV)"
| Installation |
| Variable Force Solenoind (VFS) |
Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "E-CVVT Motor"
| CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) |
Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV)"
 Catalytic Converter
Catalytic Converter
Description and operation
Description
The catalytic converter of the gasoline engine is a three way catalyst. It oxidizes
carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons (HC), and separates oxygen from the oxides
of nitrogen (NOx)...
Other information:
Hyundai Palisade (LX2) 2020-2025 Owner's Manual: Care of Seat Belts
Seat belt systems should never be disassembled or modified. In addition, care should be taken to assure that seat belts and belt hardware are not damaged by seat hinges, doors or other abuse. Periodic inspection All seat belts should be inspected periodically for wear or damage of any kind...
Hyundai Palisade (LX2) 2020-2025 Service Manual: Specifications
Specifications Smart Key Unit Items Specification Rated voltage DC 12V Operating voltage DC 9 - 16V Operating temperature -22°F to 167°F (-30°C to- 75°C) Load Max...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- 1st Generation Palisade Owners Manual
- 1st Generation Palisade Service Manual
- Check Tire Pressure
- Reverse Parking Aid Function
- Automatic Door Lock and Unlock Features
- New on site
- Most important about car
Do Not Install a Child Restraint in the Front Passenger's Seat

Even though your vehicle is equipped with the OCS, never install a child restraint in the front passenger's seat. An inflating air bag can forcefully strike a child or child restraint resulting in serious or fatal injury.
Copyright © 2025 www.hpalisadelx.com