Hyundai Palisade (LX2): Wireless Power Charger System / Wireless Power Charging Unit
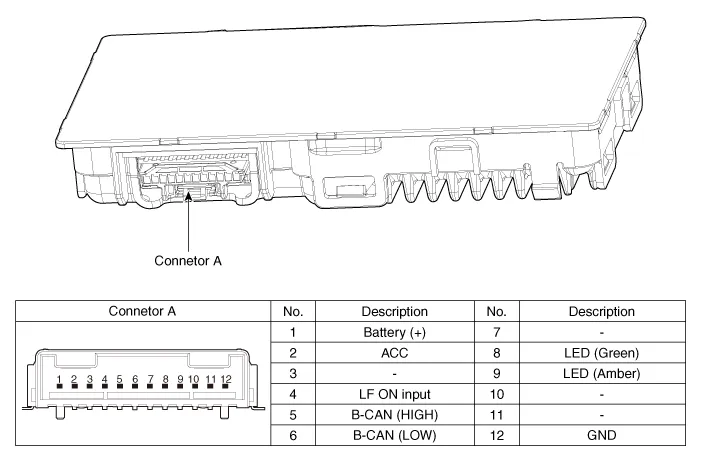
Components and positions
| Components |
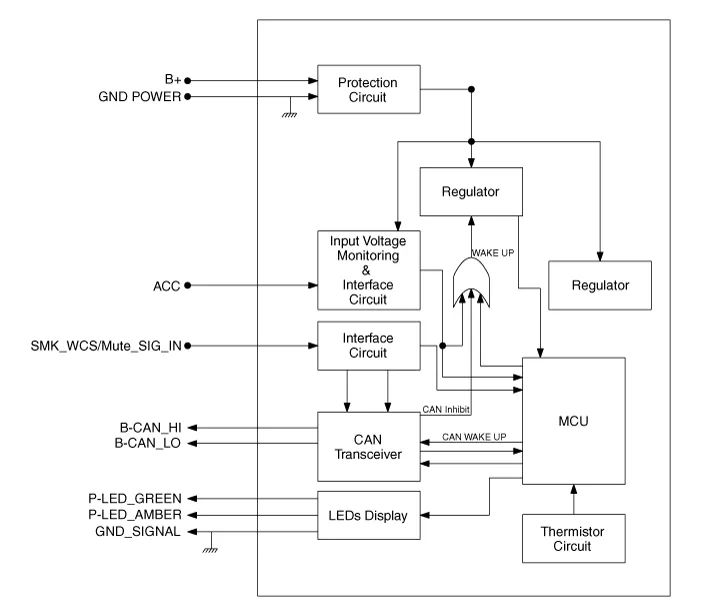
Circuit diagram
| Circuit Diagram |
Repair procedures
| Removal |
Handling wireless charging system parts by wet hands may cause electric
shock.
|
| 1. |
Disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal.
|
| 2. |
Remove the floor console cover assembly.
(Refer to Body - "Floor Console Assembly")
|
| 3. |
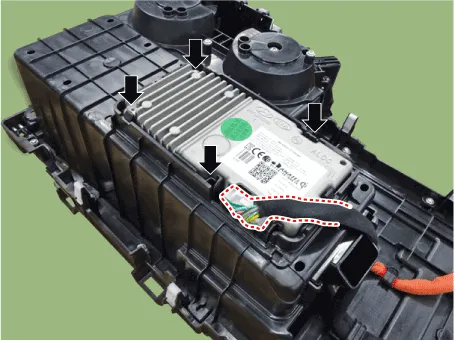
Remove the wireless power charger unit after disconnecting the connector.
|
| Installation |
| 1. |
Connect the wireless power charging unit connectors.
|
| 2. |
Install the wireless power charging unit.
|
| 3. |
Install the floor console assembly.
|
| 4. |
Connect the negative (-) battery terminal.
|
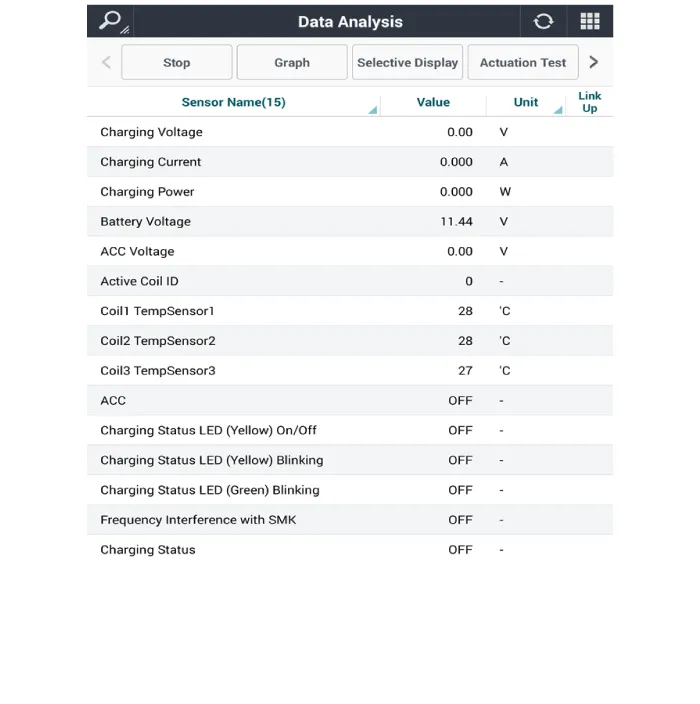
| [Diagnosis With KDS/Diagnostic tool] |
| 1. |
In the body electrical system, failure can be quickly diagnosed by using
the vehicle diagnostic system (Diagnostic tool).
The diagnostic system(Diagnostic tool) provides the following information.
|
| 2. |
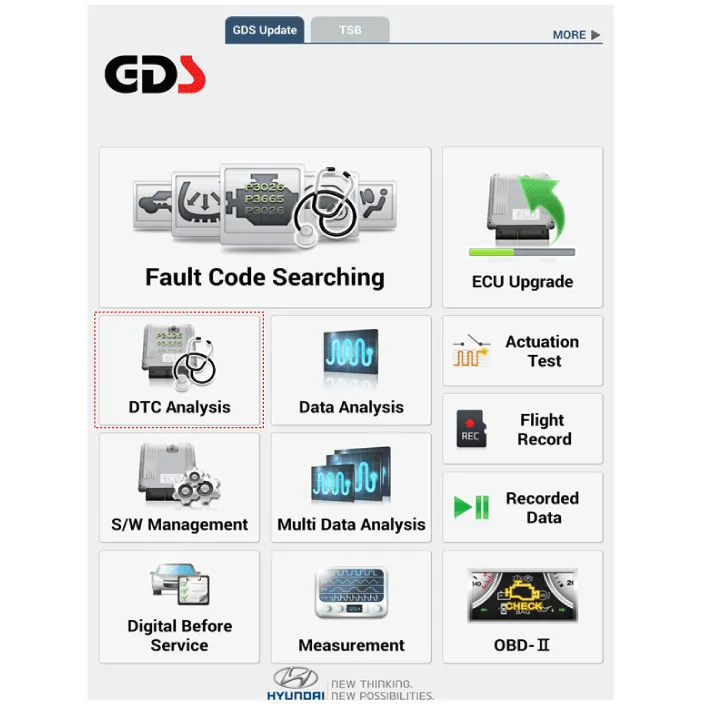
If diagnose the vehicle by Diagnostic tool, select "DTC Analysis" and
"Vehicle".
|
| 3. |
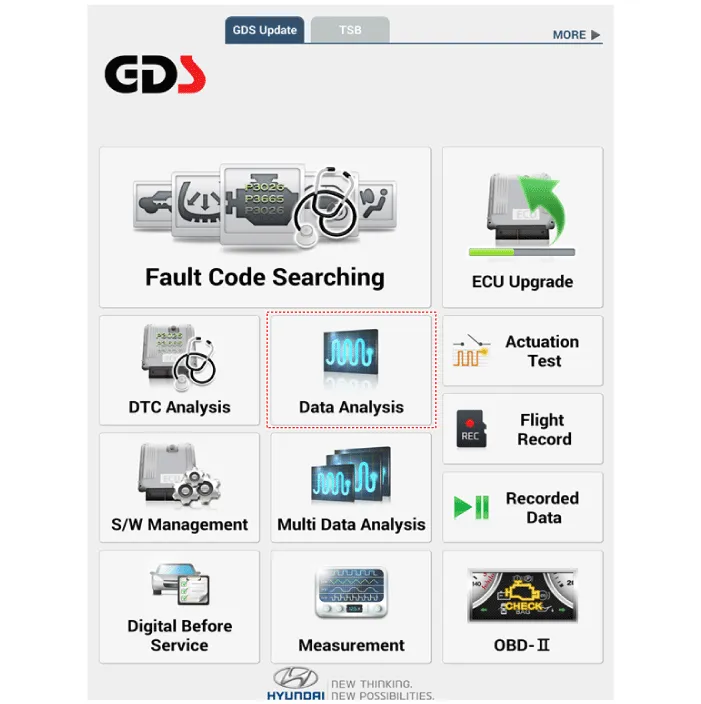
If check current status, select the "Data Analysis" .
|
| 4. |
Select the 'WPC' to search the current state of the input/output data.
|
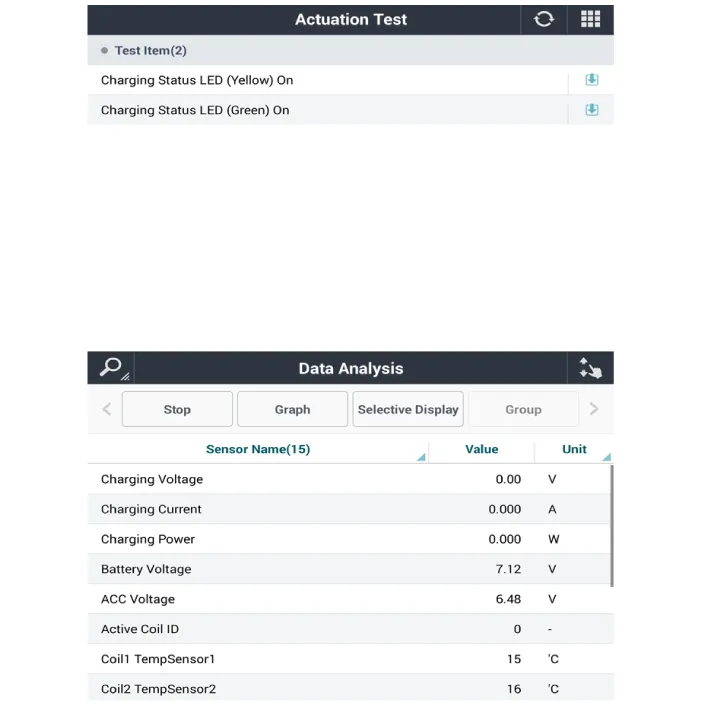
| 5. |
To forcibly actuate the input value of the module to be checked, select
option 'Actuation Test'.
|
Description and Operation Wireless Power Charger System During ACC or IG ON, battery voltage is supplied to the wireless power charger system to transmit an output of 5 W to mobile phone.
Components and positions Components Repair procedures Removal Handling wireless charging system parts by wet hands may cause electric shock.
Other information:
Hyundai Palisade (LX2) 2020-2026 Service Manual: Ambient Temperature Sensor
Description and operation Description The ambient temperature sensor is located at the front of the condenser and detects ambient air temperature. It is a negative type thermistor; resistance will increase with lower temperature, and decrease with higher temperature.
Hyundai Palisade (LX2) 2020-2026 Service Manual: Temperature Control Actuator
Description and operation Description The heater unit includes mode control actuator and temperature control actuator. The temperature control actuator is located at the heater unit. It regulates the temperature by the procedure as follows.
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Hyundai Palisade Owners Manual
- Hyundai Palisade Service Manual
- How to reset the power liftgate
- Automatic Transaxle System (A8LF1)
- Maintenance
- New on site
- Most important about car