Hyundai Palisade (LX2): Engine Control System / Accelerator Position Sensor (APS)
Description and operation
| Description |

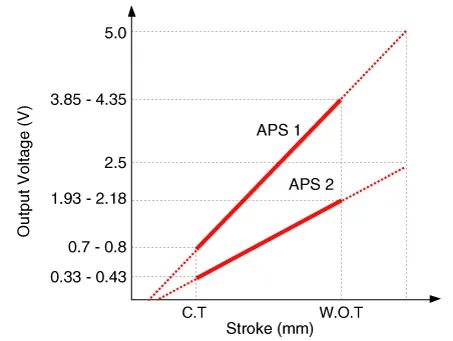
Specifications
| Specification |
|
Accelerator Position |
Output Voltage (V) [Vref = 5V] |
|
|
APS1 |
APS2 |
|
|
C.T |
0.7 - 0.8 |
0.33 - 0.43 |
|
W.O.T |
3.85 - 4.35 |
1.93 - 2.18 |
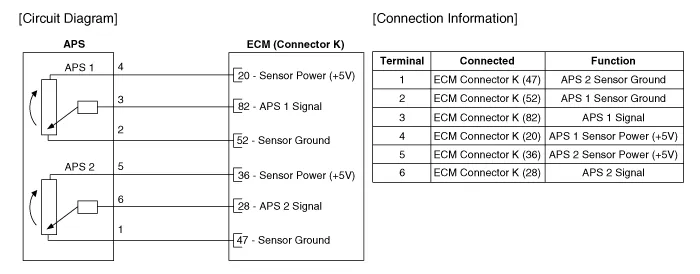
Schematic diagrams
| Circuit Diagram |
Repair procedures
| Inspection |
| 1. |
Connect the diagnostic tool on the Data Link Connector (DLC).
|
| 2. |
Switch "ON" the ignition.
|
| 3. |
Measure the output voltage of the APS 1 and 2 at C.T and W.O.T.
|
|||||||||||
| Removal |
| 1. |
Switch "OFF" the ignition and disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal.
|
| 2. |
Disconnect the accelerator position sensor connector (A).
|
| 3. |
Remove the accelerator position sensor (B) after loosening the mounting
bolts.
|
| Installation |
| 1. |
Install in the reverse order of removal.
|
Description and operation Description Continuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT) system advances or retards the valve timing of the intake and exhaust valve in accordance with the ECM control signal which is calculated by the engine speed and load.
Description and operation Description Based on information from various sensors, the ECM can calculate the fuel amount to be injected.
Other information:
Hyundai Palisade (LX2) 2020-2026 Service Manual: Rear Evaporator Core
Repair procedures Replacement 1. Remove the rear heater & A/C unit. (Refer to Rear Heater - "Rear Heater Unit") 2. Loosen the mounting screws, remove the rear heater & A/C unit cover (A) and evaporator core (B).
Hyundai Palisade (LX2) 2020-2026 Service Manual: Cruise Control (CC) Switch
Components and components location Components 1. Remote control switch (Audio swtich) 2. Remote control switch (Cruise control switch) Schematic diagrams Circuit Diagram Repair procedures Removal 1.
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Hyundai Palisade Owners Manual
- Hyundai Palisade Service Manual
- Resetting the Driver's Seat Memory System
- Removing and Storing the Spare Tire
- Lift and Support Points
- New on site
- Most important about car

